
DFS
回溯,剪枝


import java.util.*;
public class Main{
static int N = 10, n;
static int[] path = new int[N];
static boolean[] st = new boolean[N];
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
n = in.nextInt();
dfs(0);
}
public static void dfs(int u){
if(u == n){
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
System.out.print(path[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
return;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(!st[i]){
path[u] = i;
st[i] = true;
dfs(u + 1);
st[i] = false;
}
}
}
}

输入样例:
4
输出样例:
.Q..
...Q
Q...
..Q.
..Q.
Q...
...Q
.Q..
代码:
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
static int N = 10, n;
static char[][] chessboard = new char[N][N];
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
for(char[] ch : chessboard){
Arrays.fill(ch, '.');
}
n = in.nextInt();
dfs(0);
}
public static void dfs(int row){
if(row == n){
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
System.out.print(chessboard[i][j]);
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
return;
}
for(int col = 0; col < n; col++){
if(isValid(row, col)){
chessboard[row][col] = 'Q';
dfs(row + 1);
chessboard[row][col] = '.';
}
}
}
public static boolean isValid(int row, int col){
for(int i = 0; i < row; i++){
if(chessboard[i][col] == 'Q'){
return false;
}
}
for(int i = row, j = col; i >= 0 && j >= 0; i--, j--){
if(chessboard[i][j] == 'Q'){
return false;
}
}
for(int i = row, j = col; i >= 0 && j < n; i--, j++){
if(chessboard[i][j] == 'Q'){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
BFS
求解最短路问题(边权为1)
DP是特殊的最短路问题(无环)

输入样例:
5 5
0 1 0 0 0
0 1 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 1 1 1 0
0 0 0 1 0
输出样例
8
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
int m = scanner.nextInt();
int[][] matrix = new int[n][m];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
matrix[i][j] = scanner.nextInt();
}
}
int res = bfs(matrix, n, m);
System.out.print(res);
}
public static int bfs(int[][] matrix, int n, int m){
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
//将起点添加进队列
queue.offer(new Node(0, 0));
//表示从左上角开始到达当前位置走了多远距离
int[][] dis = new int[n][m];
//利用向量的方法进行上下左右前进
int[] dx = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
int[] dy = {0, 1, 0, -1};
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
//每次都处理队列的头结点
Node node = queue.poll();
//当扫描到了右下角的位置时说明搜索完毕,退出循环
if(node.x == n - 1 && node.y == m - 1) {
break;
}
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int newx = node.x + dx[i];
int newy = node.y + dy[i];
//当新位置在合法范围内并且新位置的元素为0且没有被访问过的请情况下才可以继续查找
if(newx >= 0 && newy >= 0 && newx < n && newy < m && dis[newx][newy] == 0 && matrix[newx][newy] == 0) {
//将新节点添加进队列
queue.offer(new Node(newx, newy));
//记录距离
dis[newx][newy] = dis[node.x][node.y] + 1;
}
}
}
return dis[n - 1][m - 1];
}
}
class Node{
int x;
int y;
public Node(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}

输入样例
2 3 4 1 5 x 7 6 8
输出样例
19

import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
String start = "";
for(int i = 0; i < 9; i++){
start = start + scan.next();
}
String end = "12345678x";
int res = bfs(start, end);
System.out.print(res);
}
public static int bfs(String start, String end){
//队列,用来存储状态
Queue<String> que = new LinkedList<>();
//从start走到当前状态的步数(距离)
Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
//将起点添加进队列
que.offer(start);
map.put(start,0);
int[] dx = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
int[] dy = {0, -1, 0, 1};
while(!que.isEmpty()){
String head = que.poll();
//找到k在String中的下标
int k = head.indexOf('x');
//然后进行一维数组转化成二维的下标操作
int x = k / 3 ; int y = k % 3;
int distance = map.get(head);
if(head.equals(end)){
return distance;
}
//状态转移
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
int a = x + dx[i];
int b = y + dy[i];
if(a >=0 && a < 3 && b >= 0 && b < 3){
char[] arr = head.toCharArray();
swap(arr, k, a * 3 + b);
String s = new String(arr);
if(!map.containsKey(s)){
map.put(s, distance + 1);
que.offer(s);
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
public static void swap(char[] arr,int x,int y){
char temp = arr[x];
arr[x] = arr[y];
arr[y] = temp;
}
}
树与图的存储
树是无环连通图
无向图可以转化为有向图

邻接矩阵

邻接表: 拉链法
树与图的深度优先遍历
数组建立邻接表
//邻接表
//idx 存储当前要分配的下标
static int idx;
//head数组,存储head指向的节点下标
static int[] h = new int[N];
//e[i] 存储节点i的值,即编号
static int[] e = new int[M];
//ne[i] 表示节点i的next指针,存储下标
static int[] ne= new int[M];
//头插法
static void add(int a, int b) {
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx++;
}
树与图的ddfs模板
// 需要标记数组st[N], 遍历节点的每个相邻的边
void dfs(int u) {
st[u] = true; // 标记一下,记录为已经被搜索过了,下面进行搜索过程
for (int i = h[u]; i != -1; i = ne[i]) {
int j = e[i];
if (!st[j]) {
dfs(j);
}
}
}
题目

输入样例
9
1 2
1 7
1 4
2 8
2 5
4 3
3 9
4 6
输出样例:
4
本题的本质是树的dfs, 每次dfs可以确定以u为重心的最大连通块的节点数,并且更新一下ans。
也就是说,dfs并不直接返回答案,而是在每次更新中迭代一次答案。
这样的套路会经常用到,在 树的dfs 题目中
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
//邻接表存储方式
static int N = 100010, M = N * 2, n;
//idx 存储当前要分配的下标
static int idx;
//头节点数组,存储head指向的节点下标
static int[] h = new int[N];
//e[i] 表示节点i的值
static int[] e = new int[M];
//ne[i] 表示节点i的next指针,存储下标
static int[] ne= new int[M];
//标记数组st
static boolean[] st = new boolean[N];
static int ans = N;
public static void add(int a, int b){
e[idx] = b;
ne[idx] = h[a];
h[a] = idx++;
}
//返回以u为根的子树中节点的个数,包括u节点
public static int dfs(int u){
st[u] = true;
int res = 0;
int sum = 1;
for(int i = h[u]; i != -1 ; i = ne[i]){
int j = e[i];
if(st[j] == false){
int s = dfs(j);
res = Math.max(res, s);
sum += s;
}
}
res = Math.max(res, n - sum);
ans = Math.min(res, ans);
return sum;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
n = scan.nextInt();
for(int i = 1 ; i < N ; i++ ){
h[i] = -1;
}
for(int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++){
int a = scan.nextInt();
int b = scan.nextInt();
add(a, b);
add(b, a);
}
dfs(1);
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
树与图的宽度优先遍历
层次遍历:每次pop出队时,将与它距离为1的节点全部加到队列中
树与图的bfs模板
queue <- 起点
while queue 不空
{
t <- 队头
拓展t的所有邻点s{
if(s未被遍历过){
queue <- s;
d[s] = d[t] + 1;
}
}
}
题目

输入样例:
4 5
1 2
2 3
3 4
1 3
1 4
输出样例:
1
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
static int N = 100010, n, m, idx;
static int[] e = new int[N];
static int[] ne = new int[N];
static int[] h = new int[N];
//结点1到结点i的最短距离
static int[] d = new int[N];
public static void add(int a, int b){
e[idx] = b;
ne[idx] = h[a];
h[a] = idx++;
}
public static int bfs(){
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(1);
d[1] = 0;
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
int t = q.poll();
for(int i = h[t]; i != - 1; i = ne[i]) {
int s = e[i];
if(d[s] == -1) {
q.offer(s);
d[s] = d[t] + 1;
}
}
}
return d[n];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
n = scanner.nextInt();
m = scanner.nextInt();
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
h[i] = -1;
d[i] = -1;
}
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int a = scanner.nextInt();
int b = scanner.nextInt();
add(a,b);
}
int res = bfs();
System.out.print(res);
}
}
拓扑排序
只适用于 AOV网 (有向无环图)
算法流程:
用队列来执行 ,初始化讲所有入度为0的顶点入队。
主要由以下两步循环执行,直到不存在入度为 0 的顶点为止
选择一个入度为 0 的顶点,并将它输出;
删除图中从顶点连出的所有边。
循环结束,
若输出的顶点数小于图中的顶点数,则表示该图存在回路,即无法拓扑排序,
否则,输出的就是拓扑序列 (不唯一)
queue <- 所有入度为0的点
while queue 不空
{
t <- 队头
枚举t的所有出边 t -> j{
删除t -> j, d[j]--;
if(d[j] == 0){
queue <- j;
}
}
}
题目

输入样例:
3 3
1 2
2 3
1 3
输出样例:
1 2 3
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static int N = 100010, n, m, idx;
static int[] e = new int[N];
static int[] ne = new int[N];
static int[] h = new int[N];
//数组模拟栈
static int[] q = new int[N];
//结点i的入度
static int[] d = new int[N];
public static void add(int a, int b) {
e[idx] = b;
ne[idx] = h[a];
h[a] = idx++;
}
public static boolean topSort() {
int hh = 0, tt = -1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if(d[i] == 0) {
q[++tt] = i;
}
}
while(hh <= tt) {
int t = q[hh++];
for(int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i]) {
int s = e[i];
d[s]--;
if(d[s] == 0) {
q[++tt] = s;
}
}
}
return tt == n -1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
n = in.nextInt();
m = in.nextInt();
for(int i = 0 ; i < N ; i ++ ){
h[i] = -1;
}
for(int i = 0; i< m; i++) {
int a = in.nextInt();
int b = in.nextInt();
add(a, b);
d[b]++;
}
if(topSort() == true){
for(int i = 0 ; i < n; i ++ ){
System.out.print(q[i] + " ");
}
}else {
System.out.print(-1);
}
}
}
最短路
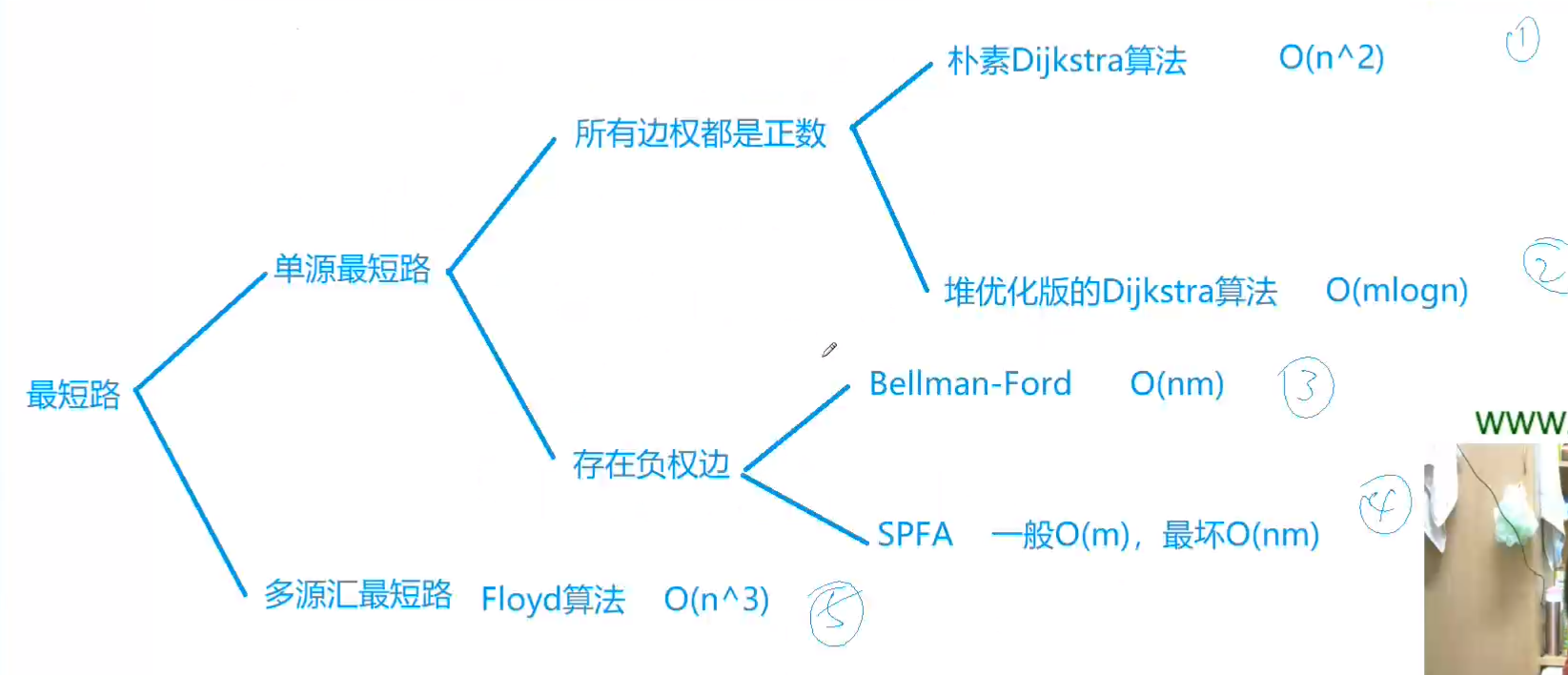
稠密图用邻接矩阵存储
稀疏图用邻接表存储

Dijkstra
Dijkstra 的整体思路:即进行n(n为结点的个数)次迭代去确定每个点到起点的最小值 最后输出的终点的即为我们要找的最短路的距离
朴素版本
适用于稠密图
集合S为已经确定最短路径的点集。
- 初始化距离
一号结点的距离为零,其他结点的距离设为无穷大(看具体的题)。 - 循环n次,每一次将集合S之外距离最短的点 t 加入到S中去(这里的距离最短指的是距离1号点最近。
点 t 的路径一定最短,基于贪心,严格证明待看)。然后用点t更新 t 邻接点的距离


输入样例:
3 3
1 2 2
2 3 1
1 3 4
输出样例:
3
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
/**
* Java快速读写模板
*/
public static StreamTokenizer in = new StreamTokenizer(new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)));
public static PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
public static BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
public static int nextInt() throws IOException {
in.nextToken();
return (int) in.nval;
}
public static double nextDouble() throws IOException {
in.nextToken();
return in.nval;
}
public static String nextString() throws IOException {
in.nextToken();
return in.sval;
}
static int N = 510, n, m;
//邻接矩阵存储图
static int[][] g = new int[N][N];
//记录每一个点距离第一个点的距离
static int [] dist = new int[N];
//用于记录该点的最短距离是否已经确定
static boolean[] st = new boolean[N];
public static int dijkstra() {
Arrays.fill(dist, 0x3f3f3f3f);
dist[1] = 0;
////迭代n次,每次可以确定一个点到起点的最短路
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int t = -1;
//t就是未确定最短路径的点的集合中距离起点最短的点
for(int j = 1; j <= n ; j++) {
if(st[j] == false && (t== -1 || dist[j] < dist[t])) {
t = j;
}
}
//加入到s集合中
st[t] = true;
//找到了距离最小的点t,并用最小的点t去更新其他的点到起点的距离
for(int j = 1 ; j <= n ; j ++ ){
dist[j] = Math.min(dist[j], dist[t] + g[t][j]);
}
}
if(dist[n] == 0x3f3f3f3f) return -1;
else return dist[n];
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
n = nextInt();
m = nextInt();
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++){
Arrays.fill(g[i], 0x3f3f3f3f);
}
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int a = nextInt();
int b = nextInt();
int z = nextInt();
//如果有重边,保留权值最小的一条边
g[a][b] = Math.min(g[a][b], z);
}
int res = dijkstra();
out.write(res + "");
out.flush();
}
}
堆优化版本
适用于稀疏图

堆优化版的dijkstra是对朴素版dijkstra进行了优化,在朴素版dijkstra中时间复杂度最高的寻找距离最短的点O(n^2)可以使用最小堆优化。
- 一号点的距离初始化为零,其他点初始化成无穷大。
- 将一号点放入堆中。
- 不断循环,直到堆空。每一次循环中执行的操作为:
弹出堆顶(与朴素版diijkstra找到S外距离最短的点相同,并标记该点的最短路径已经确定)。
用该点更新临界点的距离,若更新成功就加入到堆中。

import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
static int N = 100010;
static int n, m, idx;
static int[] h = new int[N];
static int[] e = new int[N];
static int[] ne = new int[N];
static int[] w = new int[N];
static int[] dist = new int[N];// 存储1号点到每个点的最短距离
static boolean[] st = new boolean[N];
static int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;//设置无穷大
public static void add(int a,int b,int c)
{
e[idx] = b;
w[idx] = c;
ne[idx] = h[a];
h[a] = idx ++;
}
// 求1号点到n号点的最短路,如果不存在则返回-1
public static int dijkstra()
{
//维护当前未在st中标记过且离源点最近的点
Queue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> {return a[1] - b[1];});
Arrays.fill(dist, INF);
dist[1] = 0;
queue.add(new int(1,0));
while(!queue.isEmpty())
{
//1、找到当前未在s中出现过且离源点最近的点
int[] p = queue.poll();
int t = p[0];
int distance = p[1];
if(st[t]) continue;
//2、将该点进行标记
st[t] = true;
//3、用t更新其他点的距离
for(int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if(dist[j] > distance + w[i])
{
dist[j] = distance + w[i];
queue.add(new int(dist[j], j));
}
}
}
if(dist[n] == INF) return -1;
return dist[n];
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
n = scan.nextInt();
m = scan.nextInt();
Arrays.fill(h,-1);
while(m -- > 0){
int a = scan.nextInt();
int b = scan.nextInt();
int c = scan.nextInt();
add(a,b,c);
}
int res = dijkstra();
System.out.println(res);
}
}
Bellman - ford
Bellman - ford 算法是求含负权图的单源最短路径的一种算法,效率较低,代码难度较小。其原理为连续进行松弛,在每次松弛时把每条边都更新一下,若在 n-1 次松弛后还能更新,则说明图中有负环,因此无法得出结果,否则就完成。
通俗的来讲就是:假设 1 号点到 n 号点是可达的,每一个点同时向指向的方向出发,更新相邻的点的最短距离,通过循环 n-1 次操作,若图中不存在负环,则 1 号点一定会到达 n 号点,若图中存在负环,则在 n-1 次松弛后一定还会更新
for n次
for 所有边 a,b,w (松弛操作)
dist[b] = min(dist[b],back[a] + w)
back[] 数组是上一次迭代后 dist[] 数组的备份,由于是每个点同时向外出发,因此需要对 dist[] 数组进行备份,若不进行备份会因此发生串联效应,影响到下一个点

输入样例:
3 3 1
1 2 1
2 3 1
1 3 3
输出样例:
3
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
class Edge{
int x,y,z;
public Edge(int x,int y,int z){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.z = z;
}
}
public class Main {
static int N = 510, M = 10010, n, m, k;
static int[] dist = new int[N];
static int[] back = new int[N];
static Edge[] edgs = new Edge[M];
static void bellman_ford() {
Arrays.fill(dist, (int)1e9);
dist[1] = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
back = Arrays.copyOf(dist, n + 1);
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++){
Edge edg = edgs[j]; //每一条边的结构体
int a = edg.x;
int b = edg.y;
int c = edg.z;
dist[b] = Math.min(dist[b], back[a] + c); //用上面的点来更新后面的点
}
}
if(dist[n] > (int)1e9 / 2) System.out.println("impossible");
else System.out.println(dist[n]);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
n = in.nextInt();
m = in.nextInt();
k = in.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int x = in.nextInt();
int y = in.nextInt();
int z = in.nextInt();
edgs[i] = new Edge(x, y, z);
}
bellman_ford();
}
}
SPFA
spa求最短路
Bellman_ford算法会遍历所有的边,但是有很多的边遍历了其实没有什么意义,我们只用遍历那些到源点距离变小的点所连接的边即可,只有当一个点的前驱结点更新了,该节点才会得到更新;因此考虑到这一点,我们将创建一个队列每一次加入距离被更新的结点。
SPFA算法和Dijstra算法
SPFA可以处理负权边,但是不能处理有负权回路的图;而Dijkstra不能处理带有负权边和负权回路的图,因为Dijkstra算法在计算最短路径时,不会因为负边的出现而更新已经计算过(收录过)的顶点的路径长度;
st数组
- Dijkstra算法中的st数组保存的是当前确定了到源点距离最小的点,且一旦确定了最小那么就不可逆了(不可标记为true后改变为false);
- SPFA算法中的st数组仅仅只是表示的当前发生过更新的点,且spfa中的st数组可逆(可以在标记为true之后又标记为false)。
- 顺带一提的是BFS中的st数组记录的是当前已经被遍历过的点。
队列
- Dijkstra算法里使用的是优先队列保存的是当前未确定最小距离的点,目的是快速的取出当前到源点距离最小的点;
- SPFA算法中使用的是队列(也可以使用别的数据结构),目的只是记录一下当前发生过更新的点。

输入样例:
3 3
1 2 5
2 3 -3
1 3 4
输出样例:
2
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
static int N = 100010;
static int n, m, idx;
static int[] h = new int[N];
static int[] e = new int[N];
static int[] ne = new int[N];
static int[] w = new int[N];
static int[] dist = new int[N];// 存储1号点到每个点的最短距离
static boolean[] st = new boolean[N];//判断当前的点是否已经加入到队列当中了;
static int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;//设置无穷大
public static void add(int a,int b,int c)
{
e[idx] = b;
w[idx] = c;
ne[idx] = h[a];
h[a] = idx ++;
}
// 求1号点到n号点的最短路,如果不存在则返回-1
public static void spfa()
{
Arrays.fill(dist, INF);
dist[1] = 0;
//声明一个队列保存更新过的节点
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(1);
st[1] = true;
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
int t = q.poll();
st[t] = false;
for(int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i]) {
int j = e[i];
//如果当前节点可以被更新,就做更新操作,并将该节点加入到队列中
if(dist[j] > dist[t] + w[i]) {
dist[j] = dist[t] + w[i];
if(st[j] == false) {
q.offer(j);
st[j] = true;
}
}
}
}
if(dist[n] == INF) System.out.println("impossible");
else System.out.println(dist[n]);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
n = scan.nextInt();
m = scan.nextInt();
Arrays.fill(h,-1);
while(m -- > 0){
int a = scan.nextInt();
int b = scan.nextInt();
int c = scan.nextInt();
add(a,b,c);
}
spfa();
}
}
spa求负环
统计当前每个点的最短路中所包含的边数,如果某点的最短路所包含的边数大于等于n,则也说明存在环

输入样例:
3 3
1 2 -1
2 3 4
3 1 -4
输出样例:
Yes

import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
static int N = 100010;
static int n, m, idx;
static int[] h = new int[N];
static int[] e = new int[N];
static int[] ne = new int[N];
static int[] w = new int[N];
static int[] dist = new int[N];// 存储1号点到每个点的最短距离
static boolean[] st = new boolean[N];//判断当前的点是否已经加入到队列当中了
static int[] cnt = new int[N];//1到i的最短路径边数
static int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;//设置无穷大
public static void add(int a,int b,int c)
{
e[idx] = b;
w[idx] = c;
ne[idx] = h[a];
h[a] = idx ++;
}
// 求1号点到n号点的最短路,如果不存在则返回-1
public static boolean spfa()
{
//Arrays.fill(dist, INF);
dist[1] = 0;
//声明一个队列保存更新过的节点
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
//可能起点到不了负环,所以将所有的点都加入到队列中去
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
q.offer(i);
st[i] = true;
}
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
int t = q.poll();
st[t] = false;
for(int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i]) {
int j = e[i];
//如果当前节点可以被更新,就做更新操作,并将该节点加入到队列中
if(dist[j] > dist[t] + w[i]) {
dist[j] = dist[t] + w[i];
cnt[j] = cnt[t] + 1;
if(cnt[j] >= n) return true;
if(st[j] == false) {
q.offer(j);
st[j] = true;
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
n = scan.nextInt();
m = scan.nextInt();
Arrays.fill(h,-1);
while(m -- > 0){
int a = scan.nextInt();
int b = scan.nextInt();
int c = scan.nextInt();
add(a,b,c);
}
if(spfa() == true) System.out.println("Yes");
else System.out.println("No");
}
}
Floyd
多源汇最短路问题-具有多个源点

输入样例:
3 3 2
1 2 1
2 3 2
1 3 1
2 1
1 3
输出样例:
impossible
1
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static int N = 210, INF = (int)1e9, n, m, k;
static int[][] d = new int[N][N];
/**
f[k][i][j]代表(k的取值范围是从1到n),在考虑了从1到k的节点作为中间经过的节点时,从i到j的最短路径的长度。
f[k][i][j]可以从两种情况转移而来:
【1】从f[k−1][i][j]转移而来,表示i到j的最短路径不经过k这个节点
【2】从f[k−1][i][k]+f[k−1][k][j]转移而来,表示i到j的最短路径经过k这个节点
*/
static void floyd() {
for(int k = 1; k <= n; k++) {
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
d[i][j] = Math.min(d[i][j], d[i][k] + d[k][j]);
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
n = in.nextInt();
m = in.nextInt();
k = in.nextInt();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if(i == j) d[i][j] = 0;
else d[i][j] = INF;
}
}
while(m-- > 0) {
int a = in.nextInt();
int b = in.nextInt();
int c = in.nextInt();
d[a][b] = Math.min(d[a][b], c);
}
floyd();
while(k-- > 0) {
int x = in.nextInt();
int y = in.nextInt();
if (d[x][y] > INF / 2) System.out.println("impossible");
else System.out.println(d[x][y]);
}
}
}
最小生成树

最小生成树:给定一个无向图,在图中选择若干条边把图的所有节点连起来,要求边长之和最小
应用场景:地图上,有n个城市,知道坐标,要在城市之间铺设公路,让城市相互连通,铺设最小距离是多少
Prim
prim 算法采用的是一种贪心的策略:
每次将离连通部分的最近的点和点对应的边加入的连通部分,连通部分逐渐扩大,最后将整个图连通起来,并且边长之和最小。

Prim算法与Dijkstra算法的区别:
Dijkstra算法是更新不在集合中的点 离起点的距离
dist[j]=min(dist[j], dist[t]+g[t][j])Prim是更新不在集合中的点 离集合S的距离
dist[j] = min(dist[j], g[t][j])

输入样例:
4 5
1 2 1
1 3 2
1 4 3
2 3 2
3 4 4
输出样例:
6
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
static int N = 510, INF = 0X3F3F3F3F, n, m;
static int[][] g = new int[N][N];
static int[] dist = new int[N];//点到连通部分的距离
static boolean[] st = new boolean[N];//表示节点是否已经连通
static int prim(){
Arrays.fill(dist, INF);
int res = 0;
//迭代n次找出n个点
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
int t = -1;//t表示还没有找到数
//找到离连通部分最近的点
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++){
if(!st[j] && (t == -1 || dist[j] < dist[t])){
t = j;
}
}
//第一次任选一个点为起点,不更新res
if(i > 0){
//如果这个点的距离是正无穷,说明没有连通,结束返回INF
if(dist[t] == INF) return INF;
res += dist[t];
}
st[t] = true;
//用t去更新其他集合外面的点
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++ ) dist[j] = Math.min(dist[j], g[t][j]);
}
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
n = in.nextInt();
m = in.nextInt();
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++ ){
Arrays.fill(g[i],INF);
}
while(m-- > 0){
int u = in.nextInt();
int v = in.nextInt();
int w = in.nextInt();
g[u][v] = g[v][u] = Math.min(g[u][v], w);
}
int res = prim();
if(res == INF) System.out.println("impossible");
else System.out.println(res);
}
}
Kruskal

并查集判断点a,b是否连通(属于同一集合)

输入样例:
4 5
1 2 1
1 3 2
1 4 3
2 3 2
3 4 4
输出样例:
6
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
static int N = 100010, n, m;
static int[] p = new int[N];
//并查集模板,所有的集合在过程中全部指向根节点
public static int find(int x){
if(p[x] != x) p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
static void kruskal(Edge[] g){
Arrays.sort(g, new Comparator<Edge>(){
@Override
public int compare(Edge e1, Edge e2){
return e1.c - e2.c;
}
});
int res = 0;
int cnt = 0;
//枚举所有的边
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
int a = g[i].a;
int b = g[i].b;
int c = g[i].c;
//判断一下a和b是不是在同一个集合中,不在集合中执行以下操作
a = find(a); b = find(b);
if(a != b){
p[a] = b; //将两个集合合并
res += c;//res增加权重
cnt ++;//边数加1
}
}
if(cnt < n - 1) System.out.println("impossible");
else System.out.println(res);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
n = in.nextInt();
m = in.nextInt();
Edge[] g = new Edge[m];//存储边
for(int i = 1 ; i<= n ; i ++ ) p[i] = i;
for(int i = 0 ; i < m ; i ++ ){
int u = in.nextInt();
int v = in.nextInt();
int w = in.nextInt();
g[i] = new Edge(u, v, w);
}
kruskal(g);
}
}
class Edge{
int a,b,c;
public Edge(int a, int b, int c){
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
this.c = c;
}
}
二分图



